Spaced Repetition
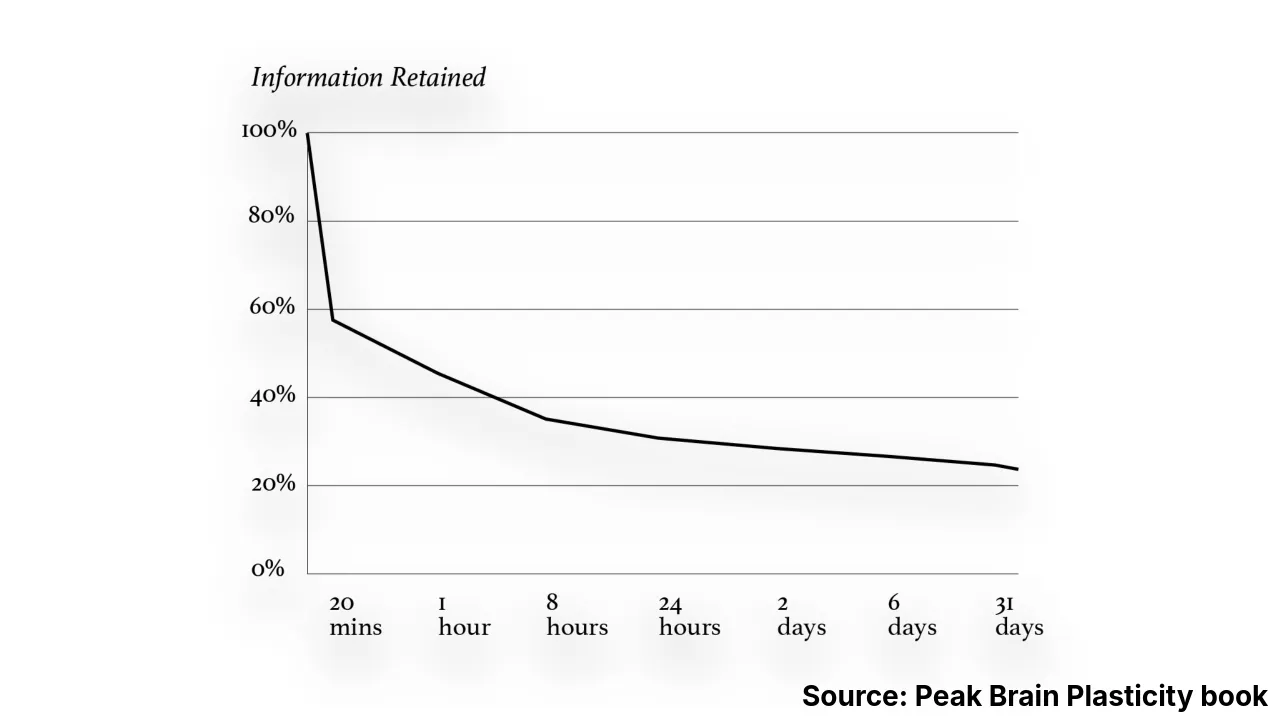
With no effort made to remember something, you will forget around 50 percent of what you learn within an hour, and 80 percent by the end of the month.
What is Spaced Repetition
Spaced repetition, also known as the spacing effect or Ebbinghaus forgetting curve, is a powerful learning technique that involves reviewing information at gradually increasing intervals, such as 10 minutes, 1 hour, 1 day, and so on. This technique is based on the groundbreaking research by Hermann Ebbinghaus, who discovered that our memory retention improves when we use spaced repetition algorithms.
The idea behind spaced repetition is that by reviewing information at increasing intervals (instead of cramming learning material in one go), we can leverage the spacing effect to improve long-term memory retention. This technique is particularly effective for learning and retaining complex or difficult information, such as language learning or mathematical formulas, and can be facilitated through flashcards.
How Spaced Repetition Works
When we encounter new information, our brains create temporary memories. However, if we do not revisit this information we have memorized, they will gradually fade according to the Ebbinghaus forgetting curve. Spaced repetition helps to prevent this forgetting by prompting us to review the information at specific time intervals, which aligns with Ebbinghaus’ research findings.
By utilizing spaced repetition, we can optimize our study sessions and maximize memory retention. For maximum impact, the review session should not occur too early when the brain can effortlessly retrieve the information, as this provides no benefit to strengthening neural pathways for future recall. However, it should also not be postponed until the information has been entirely forgotten, leaving no chance for neuropathway optimization.
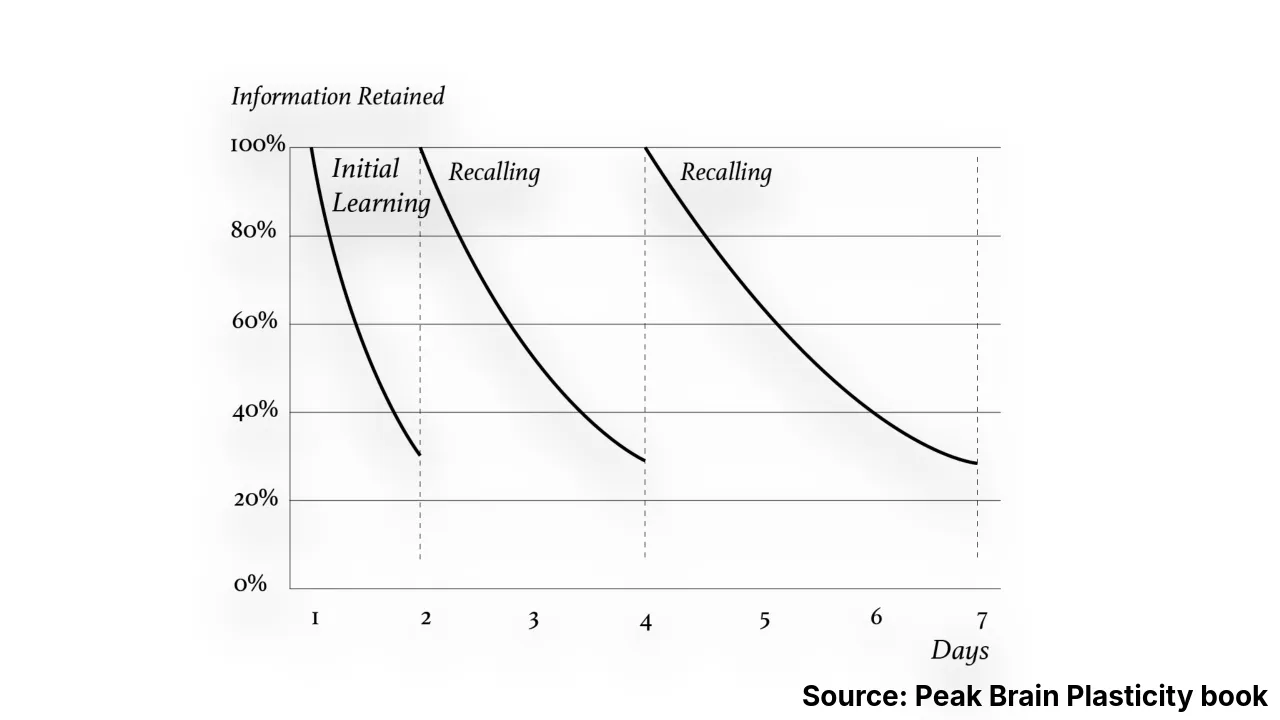 |
|---|
| Recalling Frequency |
Read more about spaced-repetition and memory upgrade from Peak Brain Plasticity book.
Benefits of Spaced Repetition
Numerous studies have proven that spaced repetition can significantly improve learning outcomes and long-term retention compared to other study techniques. Some of its benefits include:
- Improved retention
- Reduced forgetting
- Enhanced understanding
- Time efficiency
Murre, J. M., & Dros, J. (2015). Replication and analysis of Ebbinghaus’ forgetting curve. PloS one, 10(7), e0120644. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0120644
Enhanced Learning Productivity
By concentrating on reviewing your weaknesses and utilizing spaced repetition effectively, you can improve the efficiency of your learning sessions. This allows you to make the most out of your study time and maximize your long-term memory retention, ultimately enhancing your learning productivity.